Human IL-1RAcP / IL-1R3 Protein (His & Fc Tag)
C3orf13,IL-1RAcP,IL1R3
- 100ug (NPP4004) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10121-H03H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | C3orf13,IL-1RAcP,IL1R3 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human IL1R3/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer consists of 586 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 67.3 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh IL1R3/Fc monomer is approximately 75-85 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ser 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 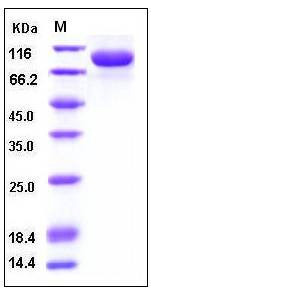 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human IL1R3 (NP_002173.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Glu 359) was fused with the C-terminal polyhistidine-tagged Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its ability to bind with biotinylated human IL1R2-His (P10111-H08H)in a functional ELISA. 2. Immobilized human IL1R3-Fch at 10 μg/mL (100ul/well) can bind biotinylated human IL1B-His (P10139-H07E). The EC50 of biotinylated human IL1B-His (P10139-H07E) is 0.11-0.25 μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Cytokine & Receptor |Interleukin & Receptor |IL-1 family & Receptor | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) also known as Interleukin-1 receptor member 3 (IL-1R3) is a a cytokine receptor which binds interleukin 1. The IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP) is a transmembrane protein that interacts with IL-1R and is required for IL-1 signal transduction. Interleukin 1 induces synthesis of acute phase and proinflammatory proteins during infection, tissue damage, or stress, by forming a complex at the cell membrane with an interleukin 1 receptor and an accessory protein. IL-1RAcP/IL-1R3 is a necessary part of the interleukin 1 receptor complex which initiates signalling events that result in the activation of interleukin 1-responsive genes. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding two different isoforms, one membrane-bound and one soluble. The ratio of soluble to membrane-bound forms increases during acute-phase induction or stress. IL-1RAcP/IL-1R3 mediates interleukin-1-dependent activation of NF-kappa-B. Isoform 1 is part of the membrane-bound form of the IL-1 receptor. Signaling involves formation of a ternary complex containing IL1R1, TOLLIP, MYD88, and IRAK1 or IRAK2. Isoform 2 modulates the response to interleukins by associating with soluble IL1R1 and enhancing interleukin-binding to the decoy receptor. |
| Reference |
