Human IL13RA1 Protein (His Tag)
CD213A1,IL-13Ra,NR4
- 100ug (NPP2271) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10943-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD213A1,IL-13Ra,NR4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human IL13Rα1 consists of 333 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 38.3 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rh IL13Rα1 is approximately 55-65 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gly 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 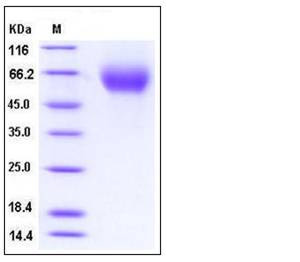 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human IL13Rα1 (NP_001551.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Thr 343) expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA . Immobilized human IL13RA1 at 4 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human IL13 with a linear ranger of 0.156-2.5 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Cytokine |Interleukins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interleukin 13 receptor, alpha 1, also known as IL13RA1/IL-13RA1 and CD213A1 (cluster of differentiation 213A1), is a subunit of the interleukin 13 receptor. This subunit forms a receptor complex with IL4 receptor alpha, a subunit shared by IL13 and IL4 receptors. IL13RA1/IL-13RA1 serves as a primary IL13-binding subunit of the IL13 receptor, and may also be a component of IL4 receptors. This protein has been shown to bind tyrosine kinase TYK2, and thus may mediate the signaling processes that lead to the activation of JAK1, STAT3 and STAT6 induced by IL13 and IL4. IL13RA1/IL-13RA1 binds with low affinity to interleukin-13 (IL13). This subunit together with IL4RA can form a functional receptor for IL13. IL13RA1/IL-13RA1 also serves as an alternate accessory protein to the common cytokine receptor gamma chain for interleukin-4 (IL4) signaling, but cannot replace the function of IL2RG in allowing enhanced interleukin-2 (IL2) binding activity. |
| Reference |
