Human IL17 / IL17A Protein
CTLA-8,CTLA8,IL-17,IL-17A,IL17
- 100ug (NPP4013) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12047-HNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | CTLA-8,CTLA8,IL-17,IL-17A,IL17 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human IL17A consists of 137 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 15.7 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 16 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 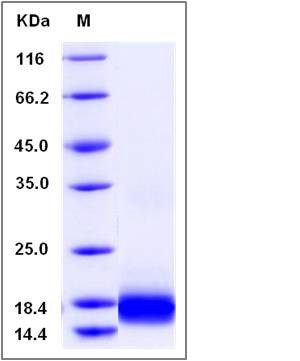 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human IL17A (Q16552) (Ile20-Ala155) was expressed, with a N-terminal Met. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to induce IL-6 secretion by HFF human foreskin fibroblast cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 15-75 ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Cytokine & Receptor |Interleukin & Receptor |IL-17 family & Receptor | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | IL17, also known as IL17a, is a cytokine belongs to the IL-17 family. Cytokines are proteinaceous signaling compounds that are major mediators of the immune response. They control many different cellular functions including proliferation, differentiation and cell survival/apoptosis but are also involved in several pathophysiological processes including viral infections and autoimmune diseases. Cytokines are synthesized under various stimuli by a variety of cells of both the innate (monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells) and adaptive (T- and B-cells) immune systems. The IL-17 family of cytokines includes six members, IL-17/IL-17A, IL-17B, IL-17C, IL-17D, IL-17E/IL-25, and IL-17F, which are produced by multiple cell types. IL-17 regulates the activities of NF-kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinases. This cytokine can stimulate the expression of IL6 and cyclooxygenase-2 (PTGS2/COX-2), as well as enhance the production of nitric oxide (NO). High levels of IL-17 are associated with several chronic inflammatory diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and multiple sclerosis. |
| Reference |
