Human IL17RD Protein (His Tag)
HH18,IL-17RD,IL17RLM,SEF
- 100ug (NPP3996) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10507-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | HH18,IL-17RD,IL17RLM,SEF |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human IL17RD comprises 294 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 33.5 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhIL17RD is approximately 55-60 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Cys 17 |
| SDS-PAGE | 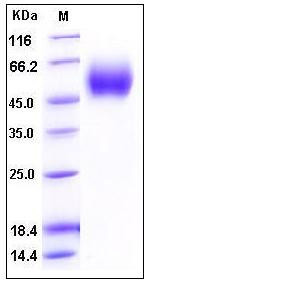 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human IL17RD (NP_060033.3) precursor (Met 1-Arg 299) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Signaling Pathway |Representative pathway |MAPK singaling Pathway |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interleukin-17 receptor D (IL-17D) also known as Interleukin-17 receptor-like protein, is a member of interleukine-17 recepter family. IL-17RD functions as a feedback inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor mediated Ras-MAPK signaling and ERK activation. It may inhibit FGF-induced FGFR1 tyrosine phosphorylation, regulate the nuclear ERK signaling pathway by spatially blocking nuclear translocation of activated ERK By similarity, and mediate JNK activation and may be involved in apoptosis. IL-17RD is found expressed in the neopallial cortex, rhombic lip and dorsal regions of the myelencephalon and in the frontal nasal process. IL-17RD is also expressed in the commissural plate and septal area of the forebrain and in the hippocampus, lens and optic cup. In the oral region, IL-17RD is expressed in the tongue and in the mesenchyme of the first branchial arch. It is also expressed in the developing inner ear. IL-17RD interacts with both IL-17R-Myc and IL-17RB-Myc. Both the intracellular and extracellular domains of IL-17RD interact with IL-17R. IL-17R forms a heteromeric complex with IL-17RD. Experiment results indicate that IL-17RD is able to affect IL-17R localization, suggesting that these two molecules are colocalized and associate with each other within cells. The fact that IL-17RD Delta ICD is unable to mediate IL-17 signaling but functions as a dominant-negative form indicates that the intracellular domain of IL-17RD is pivotal. In addition, IL-17RD interacts with the IL-17R downstream molecule TRAF6. It has been proposed that the IL-17RD intracellular domain interacts with IL-17R and TRAF6 to deliver the downstream signal. |
| Reference |
