Human IL33 / Interleukin-33 / NF-HEV Protein
C9orf26,DVS27,IL1F11,NF-HEV,NFEHEV
- 100ug (NPP1735) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10368-HNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | C9orf26,DVS27,IL1F11,NF-HEV,NFEHEV |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human IL33 comprises 160 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 18 kDa as estimated in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 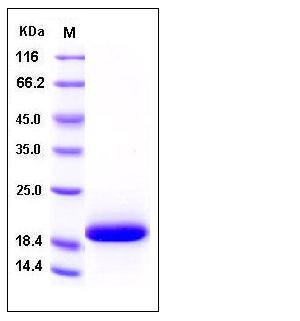 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the C-terminal segment of human IL33 (NP_254274.1) (Ser 112-Thr 270) was expressed with an initial Met at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human IL-33 at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human IL1RL1 with a linear range of 0.31-5 ng/ml. 2. Measured in a cell proliferation assay using D10.G4.1 mouse helper T cells costimulated with anti-CD3. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.15-0.6 ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Cytokines / Chemokines in Angiogenesis |Interleukins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interleukin 33 (IL-33), also known as DVS27 or NF-HEV (Nuclear Factor from High Endothelial enules), is a proinflammatory protein and a chromatin-associated cytokine of the IL-1 family with high sequence and structural similarity to IL-1 and IL-18. IL-33 protein is expressed highly and rather selectively by high endothelial venule endothelial cells (HEVECs) in human tonsils, Peyers's patches, and lymph nodes. IL-33 protein has transcriptional regulatory properties, and the researches suggested that IL-33 is a dual-function protein that might act both as a cytokine and as an intracellular nuclear factor. As a type 2 cytokines, IL-33 protein also play a pivotal role in helminthic infection and allergic disorders. |
| Reference |
