Human IL7 / interleukin 7 Protein
IL-7,Interleukin-7
- 100ug (NPP1776) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11821-HNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | IL-7,Interleukin-7 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human IL7 consists of 153 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 17.5 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 19 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 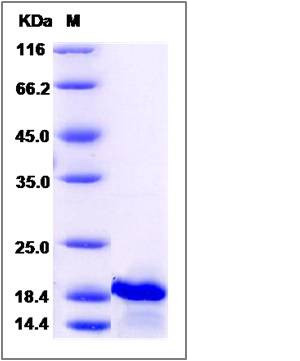 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human IL7 (Asp26-His177) was expressed with a N-terminal Met. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human IL7 at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human IL7Ra-Fch (P10975-H03H), The EC50 of human IL7Ra-Fch (P10975-H03H) is 15.2-35.6 ng/ml. 2. Measured in a cell proliferation assay using antibody against CD3-activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL). The ED50 for this effect is typically 1.2-4.7 ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Inflammatory Cytokines & Chemoki and Receptors |Common gamma Chain Receptor Family |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 25mM NaH2PO4, 400mM NaCl, pH 6.8. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | IL7, also known as interleukin 7, is a hematopoietic growth factor which belongs to the IL-7/IL-9 family. It is secreted by stromal cells in the bone marrow and thymus. IL7 stimulates the proliferation of lymphoid progenitors. It is important for proliferation during certain stages of B-cell maturation. IL7 and the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) form a heterodimer that functions as a pre-pro-B cell growth-stimulating factor. It is found to be a cofactor for V(D)J rearrangement of the T cell receptor beta (TCRß) during early T cell development. IL7 can be produced locally by intestinal epithelial and epithelial goblet cells, and may serve as a regulatory factor for intestinal mucosal lymphocytes. |
| Reference |
