Human ILKAP Protein (His Tag)
ILKAP2,ILKAP3,PP2C-DELTA
- 100ug (NPP4023) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12697-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ILKAP2,ILKAP3,PP2C-DELTA |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ILKAP comprises 403 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 44.3 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rh ILKAP is approximately 46 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 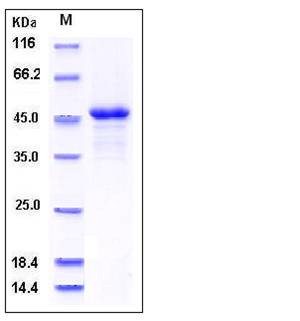 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ILKAP (Q9H0C8) (Met 1-His 392) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Protein Phosphorylation |Serine / threonine Phosphatase |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Integrin-linked kinase-associated serine/threonine phosphatase 2C, also known as ILKAP, is cytoplasm protein which belongs to the PP2C family. ILKAP contains one PP2C-like domain. ILKAP is widely expressed. Highest levels expressed in striated muscle. Much lower levels evident in various smooth muscle tissues. ILKAP may play a role in regulation of cell cycle progression via dephosphorylation of its substrates whose appropriate phosphorylation states might be crucial for cell proliferation. ILKAP selectively associates with integrin linked kinase (ILK), to modulate cell adhesion and growth factor signaling. ILKAP inhibits the ILK-GSK3B signaling axis and may play an important role in inhibiting oncogenic transformation. Integrin-linked kinase ( ILK ) plays key roles in a variety of cell functions, including cell proliferation, adhesion and migration. Within the cell, ILK localizes to multiple sites, including the cytoplasm, focal adhesion complexes that mediate cell adhesion to extracellular substrates, as well as cell-cell junctions in epidermal keratinocytes. Nuclear ILK can be rapidly exported into the cytoplasm through a CRM1-dependent pathway, and its export is enhanced by the type 2C protein phosphatase ILKAP. Nuclear localization of ILK in epidermal keratinocytes is associated with increased DNA synthesis, which is sensitive to inhibition by ILKAP. |
| Reference |
