Human ISG15 / G1P2 Protein (mature form)
G1P2,hUCRP,IFI15,IMD38,IP17,UCRP
- 100ug (NPP3882) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12729-HNAE1 |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | G1P2,hUCRP,IFI15,IMD38,IP17,UCRP |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ISG15 (mature form) consists of 157 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 17.2 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 15 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 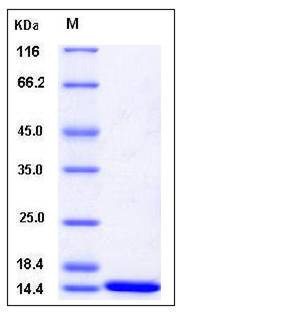 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human ISG15 (AAH09507.1) (Met 1-Gly 157) was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Cell cycle |Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway |Ubiquitin-Like Modifier |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Interferon-induced 17 kDa protein (ISG15), a 15-kDa protein of unique primary amino acid sequence, functions intracellularly as an ubiquitin homologue and a cytokine that induces production of IFN-gamma and augments NK / lymphokine-activated killer cell proliferation and function. ISG15 is secreted from monocytes and lymphocytes. ISG15 is an ubiquitin-like molecule that is strongly upregulated by type I interferons as a primary response to diverse microbial and cellular stress stimuli. Alterations in the ISG15 signalling pathway have also been found in several human tumour entities. In addition to being stimulated by type I interferon, expression of ISG15 is greatly induced by viral or bacterial infection through the Janus kinase / signal transducer and activator of transcription (Jak / STAT) signalling pathway. After induction, ISG15 is secreted by monocytes, B- and T-lymphocytes and fibroblasts. We demonstrate the novel way in which the function of the ISG15 protein is inhibited by influenza B virus, which strongly induces the ISG15 protein: a specific region of the influenza B virus NS1 protein, which includes part of its effector domain, blocks the covalent linkage of ISG15 to its target proteins both in vitro and in infected cells. |
| Reference |
