Human IZUMO1 Protein (His Tag)
IZUMO
- 100ug (NPP2284) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13520-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | IZUMO |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human IZUMO1 consists of 282 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 32.1 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 43 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Cys 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 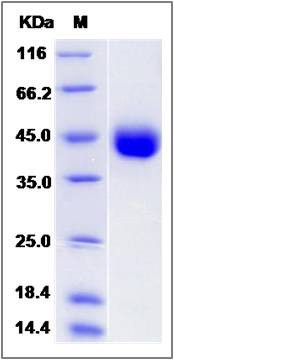 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human IZUMO1 (AAH34769.1) (Met1-Arg292) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Reproduction |Fertilization |Gamete Fusion |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Izumo is a sperm membrane protein which plays a key role in the fusion in the mouse. It has an Immunoglobulin (Ig) domain and an N-terminal domain for which neither the functions nor homologous sequences are known. Up to now, there four members has an N-terminal domain with significant homology to the N-terminal domain of Izumo. We call this domain Izumo domain. The four proteins are Izumo 1, 2, 3, and 4. Izumo domain possesses the ability to form dimers, whereas the transmembrane domain or the cytoplasmic domain or both of Izumo 1 are required for the formation of multimers of higher order. Izumo 1-3 are transmembrane proteins expressed specifically in the testis, and Izumo 4 is a soluble protein expressed in the testis and in other tissues. Izumo 1, 3, and 4 formed protein complexes on sperm, Izumo 1 forming several larger complexes and Izumo 3 and 4 forming a single larger complex. Izumo1 is essential for sperm-egg plasma membrane binding and fusion. |
| Reference |
