Human Insulin Receptor / INSR / CD220 Protein (long isoform, His Tag)
CD220,HHF5,Insulin Receptor
- 100ug (NPP4026) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11081-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD220,HHF5,Insulin Receptor |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human INSR isoform long consists of 940 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 107 (83+24) kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhINSR is approximately 125-135 kDa & 40-45 kDa, corresponding to the α subunit and the ECD of β subunit respectively in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His 28 & Ser 763 |
| SDS-PAGE | 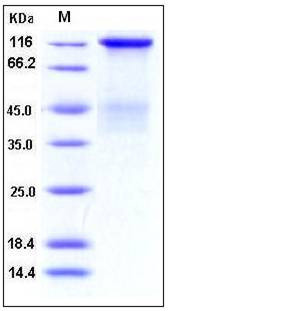 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human INSR isoform long (NP_000199.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Lys 956) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA . When 1 μg/ml of biotinylated human insulin is immobilized onto a streptavidin coated plate, it can bind human INSR (isoform long) with a linear range of 0.625-10 μg/ml . |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Cellular Senescence and Pathways in Aging |Growth Hormone/IGF-I Axis |IGF Family |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | INSR (Insulin receptor), also known as CD220, is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by insulin. INSR belongs to theprotein kinase superfamily, and exists as a tetramer consisting of two alpha subunits and two beta subunits linked by disulfide bonds. The alpha and beta subunits are encoded by a single INSR gene, and the beta subunits pass through the cellular membrane. As the receptor for insulin with tyrosine-protein kinase activity, INSR associates with downstream mediators upon binding to insulin, including IRS1 (insulin receptor substrate 1) and phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase (PI3K). IRS-1 binding and phosphorylation eventually leads to an increase in the high affinity glucose transporter (Glut4) molecules on the outer membrane of insulin-responsive tissues. INSR isoform long and isoform short are expressed in the peripheral nerve, kidney, liver, striated muscle, fibroblasts and skin, and is found as a hybrid receptor with IGF1R which also binds IGF1 in muscle, heart, kidney, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, hepatoma, fibrobasts, spleen and placenta. Defects in Insulin Receptor/INSR are the cause of Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome (Mendenhall syndrome), insulin resistance (Ins resistance), leprechaunism (Donohue syndrome), and familial hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia 5 (HHF5). It may also be associated with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). |
| Reference |
