Human Jumping Translocation Breakpoint / JTB Protein (Fc Tag)
JTB
- 100ug (NPP2287) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13447-H05H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | JTB |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human JTB/mFc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 309 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 34.7 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 38 in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Glu 31 |
| SDS-PAGE | 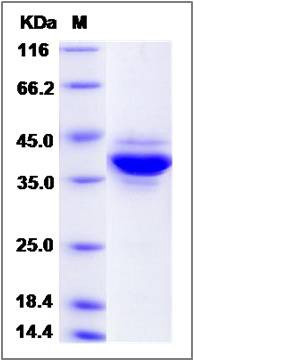 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human JTB (O76095-1) (Met1-Leu105) was fused with Fc region of mouse IgG at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Jumping translocation breakpoint, also known as JTB, is a member of the JTB family. Jumping translocation (JT) is an unbalanced translocation that comprises amplified chromosomalsegments jumping to various telomeres. JTB is expressed in all normal human tissues studied but overexpressed or underexpressed in many of their malignant counterparts. It is required for normal cytokinesis during mitosis. JTB plays a role in the regulation of cell proliferation. It may be a component of the chromosomal passenger complex (CPC), a complex that acts as a key regulator of mitosis. The CPC complex has essential functions at the centromere in ensuring correct chromosome alignment and segregation and is required for chromatin-induced microtubule stabilization and spindle assembly. |
| Reference |
