Human KEAP1 / INRF2 Protein
INRF2,KEAP-1,KLHL19
- 100ug (NPP4036) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11981-HNCB |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | INRF2,KEAP-1,KLHL19 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human KEAP1 consists of 625 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 69.7 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 64 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gly |
| SDS-PAGE | 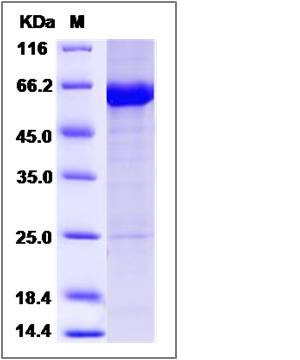 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human KEAP1 (Q14145) (Gln2-Cys624) was expressed and purified with two additional amino acids (Gly & Pro ) at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Transcription Factor & Regulator |Transcriptional Co-Repressors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 3mM DTT, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1, also known as cytosolic inhibitor of Nrf2, Kelch-like protein 19, KEAP1 and INRF2, is a cytoplasm and nucleus protein which contains one BACK (BTB/Kelch associated) domain, one BTB (POZ) domain and six Kelch repeats. KEAP1 / INRF2 is broadly expressed, with highest levels in skeletal muscle. KEAP1 / INRF2 is a key regulator of the NRF2 transcription factor, which transactivates the antioxidant response element (ARE) and upregulates numerous proteins involved in antioxidant defense. Under basal conditions, KEAP1 / INRF2 targets NRF2 for ubiquitination and proteolytic degradation and as such is responsible for the rapid turnover of NRF2. KEAP1 / INRF2 retains NFE2L2 / NRF2 in the cytosol. KEAP1 / INRF2 functions as substrate adapter protein for the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex formed by CUL3 and RBX1. It targets NFE2L2 / NRF2 for ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome, thus resulting in the suppression of its transcriptional activity and the repression of antioxidant response element-mediated detoxifying enzyme gene expression. KEAP1 / INRF2 may also retain BPTF in the cytosol. It targets PGAM5 for ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome. |
| Reference |
