Human KIR2DL4 / CD158D Protein (Fc Tag)
KIR2DL4, CD158D, KIR103AS
- 100ug (NPP2291) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13052-H02S |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | CHO Stable Cells |
| Synonyms | KIR2DL4, CD158D, KIR103AS |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human KIR2DL4/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 462 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 51.3 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 62, 34 and 32 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Trp 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 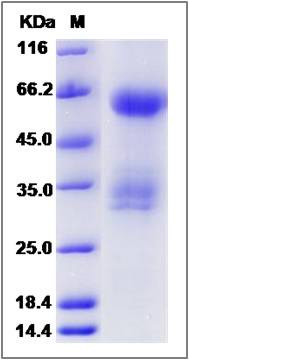 |
| Purity | (75.1+13.2+10.1) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human KIR2DL4 (ADY38409.1)(Met1-His242) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | KIR2DL4, also known as CD158d, is a member of the killer cell Ig-like receptor (KIR) family. KIRs are transmembrane glycoproteins expressed by natural killer cells and subsets of T cells. The KIR genes are polymorphic and highly homologous. KIR2DL4 is expressed in all NK cells and some T cells. KIR2DL4 activates the cytotoxicity of NK cells, despite the presence of an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif (ITIM) in its cytoplasmic tail. The ITIM was not necessary for activation of lysis by KIR2DL4. The activation signal of KIR2DL4 was sensitive to inhibition by another ITIM-containing receptor. The activation-deficient mutant of KIR2DL4 inhibited the signal delivered by the activating receptor CD16. |
| Reference |
