| Catalog Number |
P11996-H07E |
| Organism Species |
Human |
| Host |
E. coli |
| Synonyms |
C-Kit,CD117,PBT,SCFR |
| Molecular Weight |
The recombinant human KIT consists of 156 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 17.9 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 18 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N |
His |
| SDS-PAGE |
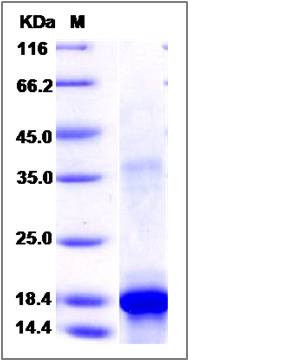 |
| Purity |
> 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction |
A DNA sequence encoding the human KIT (P10721-1) (Val50-Gln190) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity |
|
| Research Area |
Cancer |Signal transduction |Protein Kinase |Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) |
| Formulation |
Lyophilized from sterile 137mM NaCl, |
| Background |
C-Kit is a type 3 transmembrane receptor for MGF (mast cell growth factor, also known as stem cell factor). c-Kit contains 5 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains.and 1 protein kinase domain. It belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, tyr protein kinase family and CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily. C-Kit contains 5 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains and 1 protein kinase domain. C-Kit has a tyrosine-protein kinase activity. Binding of the ligands leads to the autophosphorylation of KIT and its association with substrates such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Antibodies to c-Kit are widely used in immunohistochemistry to help distinguish particular types of tumour in histological tissue sections. It is used primarily in the diagnosis of GISTs. In GISTs, c-Kit staining is typically cytoplasmic, with stronger accentuation along the cell membranes. C-Kit antibodies can also be used in the diagnosis of mast cell tumours and in distinguishing seminomas from embryonal carcinomas. Mutations in c-Kit gene are associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumors, mast cell disease, acute myelogenous lukemia, and piebaldism. Defects in KIT are a cause of acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). AML is a malignant disease in which hematopoietic precursors are arrested in an early stage of development. Note=Somatic mutations that lead to constitutive activation of KIT are detected in AML patients. |
| Reference |
Andre C, et al. (1997) Sequence analysis of two genomic regions containing the KIT and the FMS receptor tyrosine kinase genes. Genomics. 39(2):216-26. Yarden Y, et al. (1987) Human proto-oncogene c-kit: a new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 6(11):3341-51. Leong KG, et al. (2008) Generation of a prostate from a single adult stem cell. Nature. 456(7223): 804-8. Edling CE, et al. (2007) c-Kit--a hematopoietic cell essential receptor tyrosine kinase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 39(11):1995-8. McIntyre A, et al. (2005) Amplification and overexpression of the KIT gene is associated with progression in the seminoma subtype of testicular germ cell tumors of adolescents and adults. Cancer Res. 65(18):8085-9. |

