Human KLK-4 / Kallikrein-4 Protein (His Tag)
AI2A1,ARM1,EMSP,EMSP1,kallikrein,KLK-L1,PRSS17,PSTS
- 100ug (NPP4041) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11857-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | AI2A1,ARM1,EMSP,EMSP1,kallikrein,KLK-L1,PRSS17,PSTS |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human KLK4 consists of 239 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 25.8 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhKLK4 is approximately 30-35 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ser 27 |
| SDS-PAGE | 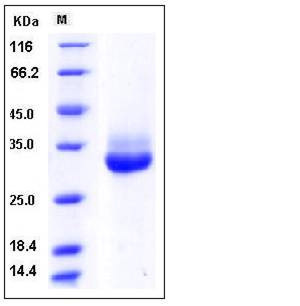 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human KLK4 (NP_004908.3) (Met 1-Ser 254) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate Boc-VPR-AMC. (R&D Systems, Catalog # ES011) . The specific activity is >250 pmoles/min/μg. (Activation description: The proenzyme needs to be activated by Thermolysin for an activated form) |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Plasma Cascade Systems in Inflammation |Fibrinolysis System |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Kallikrein-4, also known as Enamel matrix serine proteinase 1, Kallikrein-like protein 1, KLK-L1, Serine protease 17, KLK4, PRSS17 and EMSP1, is a secreted protein which belongs to the peptidase S1 family and Kallikrein subfamily. Kallikrein-4 / KLK4 is a serine protease expressed during enamel maturation, and proteolytic processing of the enamel matrix by KLK4 is critical for proper enamel formation. Kallikrein-4 / KLK4 contains one peptidase S1 domain. Kallikrein-4 / KLK4 is secreted by transition- and maturation-stage ameloblasts. KLK4 aggressively degrades the retained organic matrix following the termination of enamel protein secretion. Two proteases are secreted into the enamel matrix of developing teeth. The early protease is enamelysin (MMP-20). The late protease is kallikrein 4 (KLK4). The principle functions of MMP-20 and KLK4 in dental enamel formation are to facilitate the orderly replacement of organic matrix with mineral, generating an enamel layer that is harder, less porous, and unstained by retained enamel proteins. Defects in Kallikrein-4 / KLK4 are the cause of amelogenesis imperfecta hypomaturation type 2A1 (AI2A1) which is an autosomal recessive defect of enamel formation. The disorder involves both primary and secondary dentitions. |
| Reference |
