Human KLK13 / Kallikrein-13 Protein (His Tag)
KLK-L4,KLKL4
- 100ug (NPP2296) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10199-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | KLK-L4,KLKL4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human KLK13 consists of 256 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 28.4 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rh KLK13 is approximately 33-37 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gly 18 |
| SDS-PAGE | 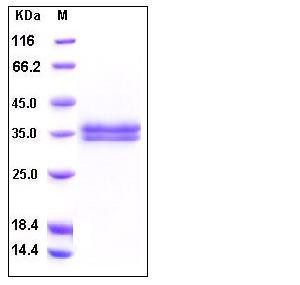 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the pro-form of human KLK13 (NP_056411.1) (Met 1-Ile 262) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate Boc-VPR-AMC (R&D Systems, Catalog # ES011) . The specific activity is >200 pmoles/min/μg. (Activation description: The proenzyme needs to be activated by Lysyl-Endopeptidase for an activated form) |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Complement and Coagulation |Plasmin/Plasminogen and Kallikrein/Kinin Systems |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Human tissue kallikrein 13 (hK13), also known as KLK-L4 (kallikrein-like gene 4), is a member of the human tissue kallikrein family of serine proteases having diverse physiological functions in many tissues. The KLK13 gene resides on chromosome 19q13.3-4 along with other 14 members in a gene cluster and shares a high degree of homology. KLK13 is a trypsin-like, secreted serine protease expressed specifically in the testicular tissue including prostate, salivary gland, breast, and testis. Growing evidence suggests that many kallikreins are implicated in carcinogenesis and may play a role in metastasis. KLK13 may be involved in the pathogenesis and/or progression of breast and ovary cancers, and is regarded as a novel cancer biomarker. In addition, KLK13 interacts and forms complexes with several serum protease inhibitors, such as alpha2-macroglobulin, and its expression is regulated by steroid hormones. |
| Reference |
