Human KNG1 / BDK / Kininogen-1 Protein (His Tag)
BDK,BK,KNG
- 100ug (NPP4045) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10529-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | BDK,BK,KNG |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human KNG1 consists of 637 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 71.3 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhKNG1 is approximately 100-110 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 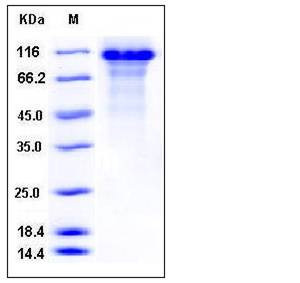 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human KNG1 isoform 1 (NP_001095886.1) (Gln 19-Ser 644) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus, and a signal peptide at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit papain cleavage of a fluorogenic peptide substrate Z-FR-AMC, R&D Systems, Catalog # ES009 . The IC50 value is < 7 nM . |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolism processes |Apoptosis | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 25mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Mouse kininogen-1, also known as high molecular weight kininogen, williams-Fitzgerald-Flaujeac factor, Alpha-2-thiol proteinase inhibitor, Fitzgerald factor, KNG1 and BDK, is a secreted protein which contains three cystatin domains. Kininogen-1 / KNG1 is a protein from the blood coagulation system as well as the kinin-kallikrein system. It is a protein that adsorbs to the surface of biomaterials that come in contact with blood. Kininogen-1 / KNG1 circulates throughout the blood and quickly adsorbs to the material surfaces. Kininogen-1 / KNG1 is one of the early participants of the intrinsic pathway of coagulation, together with Factor XII (Hageman factor) and prekallikrein. Kininogen-1 / KNG1 is one of the kininogens, a class of proteins. As with many other coagulation proteins, the protein was initially named after the patients in whom deficiency was first observed. When the clinical data were combined, it turned out that all patients, in fact, had a deficiency of the same protein. Defects in KNG1 are the cause of high molecular weight kininogen deficiency (HMWK deficiency) which is an autosomal recessive coagulation defect. Patients with HWMK deficiency do not have a hemorrhagic tendency, but they exhibit abnormal surface-mediated activation of fibrinolysis. |
| Reference |
