Human KSP-Cadherin / Cadherin-16 / CDH16 Protein (His Tag)
UNQ695/PRO1340
- 100ug (NPP4046) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10915-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | UNQ695/PRO1340 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CDH16 comprises 779 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 84.8 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 100 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Lys 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 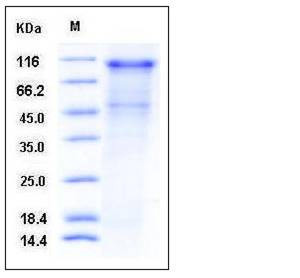 |
| Purity | > 70 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human CDH16 (NP_004053.1) (Met 1-Ala 786) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of MCF-7 human breast adenocarcinoma cells. When cells are added to CDH16-His coated plates (10 μg/mL, 100 μL/well), approximately 20-40% will adhere specifically after 60 minutes at 37 ℃. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Adhesion molecule |Cell adhesion |Cadherins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | KSP-Cadherin/Cadherin-16 is a member of the cadherin superfamily, calcium-dependent, membrane-associated glycoproteins. The protein consists of an extracellular domain containing 6 cadherin domains, a transmembrane region and a truncated cytoplasmic domain but lacks the prosequence and tripeptide HAV adhesion recognition sequence typical of most classical cadherins. Expression is exclusively in kidney, where the protein functions as the principal mediator of homotypic cellular recognition, playing a role in the morphogenic direction of tissue development. KSP-Cadherin/Cadherin-16 can be detected at later stages of tubulogenesis during human renal development and in the distal tubules of adult kidneys, no expression was found by immunohistochemistry or Western blot analysis in RCC tumour tissues and several RCC cell lines. However, despite the lack of protein expression, mRNA synthesis of KSP-Cadherin/Cadherin-16 could be detected by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis in all RCC tissues and most of the RCC cell lines studied, although at a reduced level. The loss of KSP-Cadherin/Cadherin-16 protein was only observed in the malignant part of the tumour kidneys, whereas in the normal part of the affected kidneys KSP-Cadherin/Cadherin-16 expression was clearly detected. These results indicate a downregulation of Ksp-cadherin in RCC and suggest a role for this cell adhesion molecule in tumour suppression. |
| Reference |
