Human L-FABP / FABP1 Protein (His Tag)
FABPL,L-FABP
- 100ug (NPP2298) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12353-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | FABPL,L-FABP |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human FABP1 consisting of 137 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 15.6 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 15 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 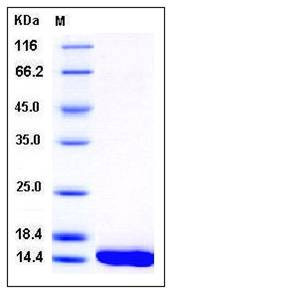 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human FABP1 (NP_001434.1) (Ser 2-Ile 127) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Microbiology |Pathogenic microorganism |viruses |animal virus |viral illness |Central nervous system diseases | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 8.3 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Fatty acid-binding protein, liver, also known as Fatty acid-binding protein 1, Liver-type fatty acid-binding protein, FABP1 and FABPL,is a cytoplasm protein which belongs to the calycin superfamily and Fatty-acid binding protein (FABP) family. Fatty acid binding proteins are a family of small, highly conserved, cytoplasmic proteins that bind long-chain fatty acids and other hydrophobic ligands. FABP1 and FABP6 (the ileal fatty acid binding protein) are also able to bind bile acids. It is thought that FABPs roles include fatty acid uptake, transport, and metabolism. FABP1 / FABPL binds free fatty acids and their coenzyme A derivatives, bilirubin, and some other small molecules in the cytoplasm. It forms a beta-barrel structure that accommodates hydrophobic ligands in its interior. FABP1 / FABPL may be involved in intracellular lipid transport. |
| Reference |
