Human LAIR2 / CD306 Protein
CD306,LAIR2,MGC71634,XXbac-BCX535A19.6
- 100ug (NPP2301) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10868-HNAH |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD306,LAIR2,MGC71634,XXbac-BCX535A19.6 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human LAIR2 comprises 131 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 14.1 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rh LAIR2 is approximately 22 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 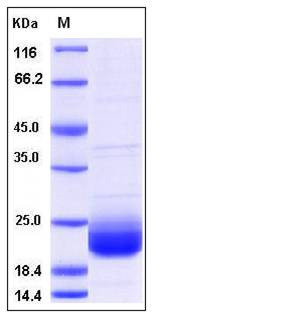 |
| Purity | > 93 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human LAIR2 (NP_002279.2) (Met 1-Pro 152) was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma cells . When 5 x 10E4 cells/well are added to recombiannt human LAIR2 coated plates (50 μg/ml with 100 μl/well), >30% will adhere after 30 minutes at 37℃. Optimal concentration depends on cell type as well as the application or research objectives. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Monocytes/Macrophages |Monocyte Markers |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 0.7M NaCl, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor 2 ( LAIR2 ), also known as CD306, is a 131 amino acid protein containing one lg-like C2-type domain. It is expressed as a soluble receptor exhibiting high affinity for various collagen molecules to which it binds in a hydroxyproline-dependent manner. LAIR2 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and was identified by its similarity to LAIR1, an inhibitory receptor present on mononuclear leukocytes. LAIR2 is thought to be secreted and may help modulate mucosal tolerance. As a natural competitor for LAIR1, soluble LAIR2 prevents binding of human LAIR1 to collagens and LAIR1 cross-linking, thereby regulating its inhibitory potential. Accordingly, LAIR2 is suggested to perform an immunoregulatory function. |
| Reference |
