Human LBP / Lipopolysaccharide binding Protein (His Tag)
BPIFD2
- 100ug (NPP2311) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10526-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | BPIFD2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human LBP consists of 467 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 52.5 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhLBP is approximately 62 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ala 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 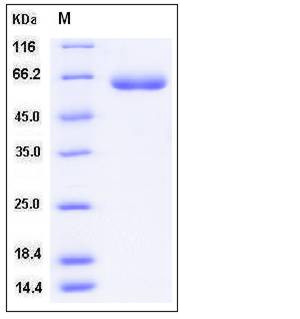 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human LBP (NP_004130.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Val 481) was fused with the a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Cancer Metabolism |Metabolic signaling |Metabolism of lipids and lipoprotein |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 0.05mM EDTA, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Lipopolysaccharide binding protein ( LBP ) is a glycoprotein that is synthesized principally by hepatocytes. LBP is a trace plasma protein that binds to the lipid A moiety of bacterial lipopolysaccharides ( LPSs ). LBP binds directly to the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and to purified aggregates of extracted endotoxin, and catalyses the delivery of endotoxin to membrane ( mCD14,GPI-Linked ) and soluble ( sCD14 ) forms of CD14, thereby markedly increasing host cell sensitivity to endotoxin. LBP efficiently catalyses the transfer of individual molecules of endotoxin to (s)CD14 only when LBP–endotoxin aggregates are formed in the presence of albumin. In the presence of EDTA, LBP binding promotes further disaggregation of endotoxin. LBP binding does not have such drastic effects under more physiological conditions, but may still induce more subtle topological rearrangements of endotoxin. |
| Reference |
