Human LCN1 / VEGP / Lipocalin-1 Protein (His Tag)
MGC71975,PMFA,TLC,TP,VEGP
- 100ug (NPP4053) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11583-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | MGC71975,PMFA,TLC,TP,VEGP |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human LCN1 consists of 169 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 19 kDa The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 20 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 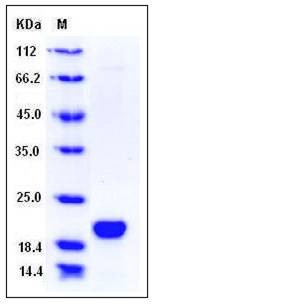 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human LCN1 (NP_002288.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Asp176) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit active Cathepsin V cleavage of a fluorogenic peptide substrate Z-LR-AMC, (R&D Systems, Catalog # ES008) . The IC50 value is < 400 nM . |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Atherosclerosis |Vascular Inflammation |Inflammatory mediators |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Lipocalin-1, also known as Von Ebner gland protein, VEG protein, Tear prealbumin, VEGP, Tear lipocalin and LCN1, is a secreted protein which belongs to the calycin superfamily and Lipocalin family. Human Lipocalin-1 / VEGP was originally described as a major protein of human tear fluid, which was thought to be tear specific. Lipocalin-1 / VEGP is identical with lingual von Ebner's gland protein, and is also produced in prostate, nasal mucosa and tracheal mucosa. Homologous proteins have been found in rat, pig and probably dog and horse. Lipocalin-1 / VEGP is an unusual lipocalin member, because of its high promiscuity for relative insoluble lipids and binding characteristics that differ from other members. Lipocalin-1 / VEGP acts as the principal lipid binding protein in tear fluid, a more general physiological function has to be proposed due to its wide distribution and properties. Lipocalin-1 / VEGP would be ideally suited for scavenging of lipophilic, potentially harmful substances and thus might act as a general protection factor of epithelia. Lipocalin-1 / LCN1 could play a role in taste reception. It could be necessary for the concentration and delivery of sapid molecules in the gustatory system. Lipocalin-1 / LCN1 can bind various ligands, with chemical structures ranging from lipids and retinoids to the macrocyclic antibiotic rifampicin and even to microbial siderophores. It exhibits an extremely wide ligand pocket. |
| Reference |
