Human LIF Protein
CDF,DIA,HILDA,Leukemia Inhibitory Factor,MLPLI
- 100ug (NPP1642) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14890-HNAH |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CDF,DIA,HILDA,Leukemia Inhibitory Factor,MLPLI |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human LIF comprises 180 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 19.7 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 35.4 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ser 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 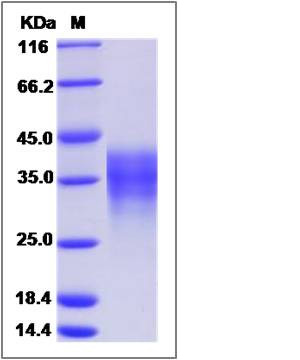 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human LIF (P15018) (Met1-Phe202) was expressed. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit the proliferation of M1 mouse myeloid leukemia cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.2-0.8 ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cytokines & Growth Factors |Cytokine & Receptor |Interleukin & Receptor |IL-6 family & Receptor |IL-6 family ligand | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) is a pleiotropic glycoprotein belonging to the IL-6 family of cytokines. It’s involved in growth promotion and cell differentiation of different types of target cells, influence on bone metabolism, cachexia, neural development, embryogenesis and inflammation. LIF has potent proinflammatory property, being the inducer of the acute phase protein synthesis and affecting the cell recruitment into the area of damage or inflammation. LIF is also one of the cytokines that are capable to regulate the differentiation of embryonic stem cells, hematopoietic and neuronal cells. LIF binds to the specific LIF receptor (LIFR-α) which forms a heterodimer with a specific subunit common to all members of that family of receptors, the GP130 signal transducing subunit. This leads to activation of the JAK/STAT and MAPK cascades. Due to its polyfunctional activities, LIF is involved in the pathogenic events and development of many diseases of various origin. |
| Reference |
