Human LOXL2 / Lysyl oxidase homolog 2 Protein (His Tag)
LOR2,Lysyl oxidase-like 2,WS9-14
- 100ug (NPP3953) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11664-H08S |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | CHO Stable Cells |
| Synonyms | LOR2,Lysyl oxidase-like 2,WS9-14 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human LOXL2 consists of 760 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 85.5 kDa. |
| predicted N | Gln 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 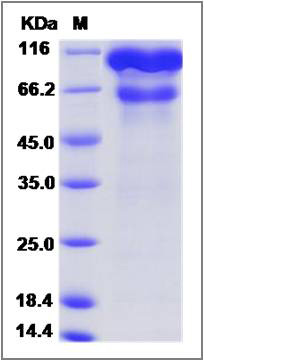 |
| Purity | (67+30) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human LOXL2 (Q9Y4K0) (Met1-Gln774) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to produce hydrogen peroxide during the oxidation of benzylamine. The specific activity is >2pmol/min/μg |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Transcription Factors and Regulators |HIF Transcription Factors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20 mM MES, 50 mM NaCl 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Lysyl oxidase homolog 2, also known as Lysyl oxidase-like protein 2, Lysyl oxidase-related protein 2, Lysyl oxidase-related protein WS9-14 and LOXL2, is a secreted protein which belongs to the lysyl oxidase family. LOXL2 contains four SRCR domains. The lysyl oxidase family is made up of five members: lysyl oxidase (LOX) and lysyl oxidase-like 1-4 ( LOXL1, LOXL2, LOXL3, LOXL4 ). All members share conserved C-terminal catalytic domains that provide for lysyl oxidase or lysyl oxidase-like enzyme activity; and more divergent propeptide regions. LOX family enzyme activities catalyze the final enzymatic conversion required for the formation of normal biosynthetic collagen and elastin cross-links. LOXL2 is expressed by pre-hypertrophic and hypertrophic chondrocytes in vivo, and that LOXL2 expression is regulated in vitro as a function of chondrocyte differentiation. LOXL2 promotes chondrocyte differentiation by mechanisms that are likely to include roles as both a regulator and an effector of chondrocyte differentiation. LOXL2 expression could also be explored as a molecular target in the prevention of breast cancer progression. |
| Reference |
