Human LRRTM4 Protein (His Tag)
UNQ3075/PRO9907, FLJ12568, MGC120633, MGC120636
- 100ug (NPP4064) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11387-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | UNQ3075/PRO9907, FLJ12568, MGC120633, MGC120636 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human LRRTM4 consists of 405 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 46.6 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh LRRTM4 is approximately 65 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 31 |
| SDS-PAGE | 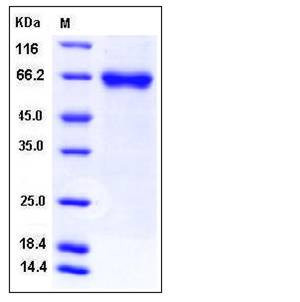 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human LRRTM4 extracellular domain (NP_001128217.1) (Met 1-Lys 424) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Cadherins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Leucine-rich repeat transmembrane neuronal protein 4, also known as LRRTM4, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the LRRTM family. LRRTM4 is expressed in the limb mesenchyme, neural tube, caudal mesoderm and in three distinct regions of the head. LRRTM4 may play a role in the development and maintenance of the vertebrate nervous system. Leucine-rich repeat containing proteins are involved in protein-protein interactions and they regulate numerous cellular events during nervous system development and disease. Human and mouse LRRTMs are highly conserved, and orthologous genes exist in other vertebrates but not in invertebrates. LRRTM mRNAs are predominantly expressed in the nervous system and that each LRRTM possesses a specific, partially nonoverlapping expression pattern. The structure and expression profile of LRRTM mRNAs suggest that they may have a role in the development and maintenance of the vertebrate nervous system. All LRRTMs, except LRRTM4, are located in the introns of different alpha-catenin genes, suggesting coevolution of these two gene families. |
| Reference |
