Human LSAMP Protein (His Tag)
FLJ34254,FLJ35396,FLJ37216,FLJ54658,IGLON3,LAMP
- 100ug (NPP2320) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12136-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | FLJ34254,FLJ35396,FLJ37216,FLJ54658,IGLON3,LAMP |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted mature form of recombinant human LSAMP consists of 298 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 33.4 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhLSAMP is approximately 45-55 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Val 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 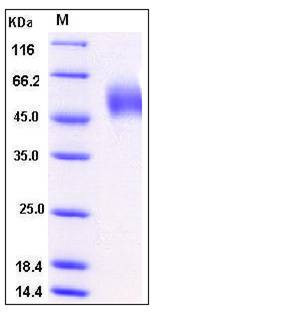 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human LSAMP (Q13449) (Met 1-Asn 315), without the pro peptide, was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Protein Trafficking |Organelle Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The limbic system-associated membrane protein (LAMP) is a cell surface glycoprotein expressed by cortical and subcortical regions of the mammalian CNS that comprise or receive direct projections from limbic system structures. The 64-68-kDa glycoprotein limbic system-associated membrane protein (LsAMP) is expressed on the surface of somata and proximal dendrites of neurons. These areas perform cognitive and autonomic functions, also learning and memory. The functional analysis indicates that LsAMP acts as a selective adhesion molecule, serving as a guidance cue for specific patterns of connectivity, which underlies the normal development of the limbic system. In animal studies there have been found that rats with increased level of anxiety had 1.6-fold higher expression of LsAMP gene in the periaqueductal gray compared to rats with low level of anxiety, indicating a possible role of LsAMP in the regulation of anxiety. |
| Reference |
