Human LY86 / MD-16 Protein (Fc Tag)
dJ80N2.1,MD-1,MD1,MMD-1
- 100ug (NPP2337) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10242-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | dJ80N2.1,MD-1,MD1,MMD-1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human LY86/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 383 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 42.7 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 48 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions |
| predicted N | Gly 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 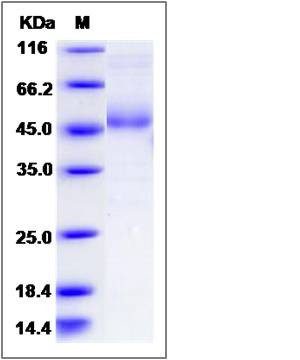 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human LY86 (O95711) (Met1-Ser162) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Cells Involved in Inflammation |Monocyte/Macrophage |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | MD-1 and MD-2 are secretory glycoproteins that exist on the cell surface in complexes with transmembrane proteins. MD-1 is anchored by radioprotective 105 (RP105) which is a molecule containing leucine-rich repeats and is expressed on B cells, dentritic cells and macrophages, while MD-2 is associated with TLR4. MD-1 is required for efficient RP105 cell surface expression and function. It is indicated that the RP105/MD1 complex, in conjunction with TLR4, mediates the innate immune response to LPS in B cells, and also plays a role in protecting against apoptosis, B-cell proliferation, etc. Mouse MD-1 cDNA encodes a 162 amino acid precursor protein with a putative 19 aa signal peptide and two potential N-linked glycosylation sites. It shares 40% and 66% amino acid sequence identity with chicken and human MD-1 respectively. MD-1 is mainly expressed in spleen, and also detectable in liver, brain, thymus, and kidney. |
| Reference |
