Human Lck Kinase Protein (GST Tag)
IMD22,LSK,p56lck,pp58lck,YT16
- 100ug (NPP4052) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10043-H09B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | IMD22,LSK,p56lck,pp58lck,YT16 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human LCK/GST chimera consists of 734 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 84.4 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 80 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 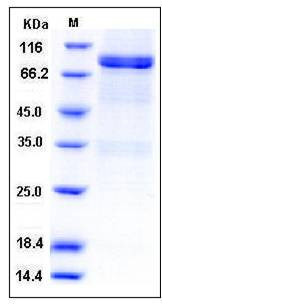 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human LCK (NP_001036236.1) (Met 1-Pro 509) was fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. The specific activity was determined to be 70 nmol/min/mg using Poly(Glu,Tyr) 4:1 as substrate. 2. Measured by its ability to bind recombinant human CD3E in a functional ELISA. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Jak/STAT Signaling |Src Kinases |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 0.5mM GSH, 0.1mM EGTA, 0.1mM EDTA, 0.5mM PMSF, 10% glycerol 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Protein kinases are critically involved in signaling pathways that regulate cell growth, differentiation, activation, and survival. Initially identified as a T-cell specific member of the Src family of protein tyrosine kinases, Lck has become the object of intensive investigations which have revealed a key role for this kinase in the central processes controlling T-cell development, activation, proliferation and survival. Lck is expressed specifically in lymphoid cells. It contains one protein kinase domain, one SH2 domain, and one SH3 domain. It is associated with a variety of cell surface receptors and is critical for signal transduction from the T-cell antigen receptor (TCR). Consequently, Lck is targeted by regulatory proteins of T-lymphotropic viruses, especially by the Herpesvirus saimiri (HVS) tyrosine kinase interacting protein (Tip). This oncoprotein physically interacts with Lck in HVS transformed T cells and has an impact on its catalytic activity. Together with the identification of defects in the regulation of Lck expression or activity in T-cell leukemias, suggests that dysregulation of Lck might play a role in neoplastic transformation. However, under certain conditions Lck is also involved in the induction of apoptosis. This chemosensitizing effect of Lck is independent of T-cell receptor signaling and does not require the kinase activity of Lck. The findings demonstrate that Lck might be part of two independent signaling pathways leading to either cell proliferation or apoptosis. |
| Reference |
