Human Leukotriene A4 Hydrolase / LTA4H Protein (His Tag)
LAT4
- 100ug (NPP4058) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10276-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | LAT4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human LTA4H consists of 621 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 70.7 kDa. It migrates as approximately 58-68 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 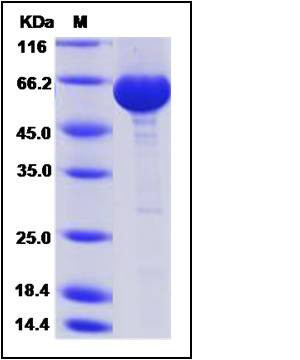 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human LTA4H (NP_000886.1) (Met1-Asp611) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate, Arg-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin(R-AMC). The specific activity is > 15 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Atherosclerosis |Vascular Inflammation |Inflammatory mediators |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Mouse leukotriene A-4 hydrolase, also known as LTA-4 hydrolase, Leukotriene A (4) hydrolase, LTA4H and LTA4, is cytoplasm protein which belongs to the peptidase M1 family. LTA4H hydrolyzes an epoxide moiety of leukotriene A4 (LTA-4) to form leukotriene B4 (LTB-4). This enzyme also has some peptidase activity. The leukotrienes (LTs) are a class of structurally related lipid mediators involved in the development and maintenance of inflammatory and allergic reactions. In the biosynthesis of LTs, arachidonic acid was converted into the unstable intermediate epoxide LTA4, which may in turn be conjugated with glutathione to form the spasmogenic LTC4, or hydrolyzed into the proinflammatory lipid mediator LTB4 in a reaction catalyzed by Leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H). LTB4 is a classical chemoattractant of human neutrophils and triggers adherence and aggregation of leukocytes to vascular endothelium, and also modulates immune responses. As a bifunctional zinc metalloenzyme, LTA4H also exhibits an anion-dependant arginyl aminopeptidase activity of high efficiency and specificity in addition to its epoxide hydrolase activity. LTA4H is regarded as a therapeutic target for inflammation. |
| Reference |
