Human Lumican / LUM Protein (His Tag)
LDC,SLRR2D
- 100ug (NPP4066) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11640-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | LDC,SLRR2D |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human LUM consists of 331 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 38 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 45-55 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 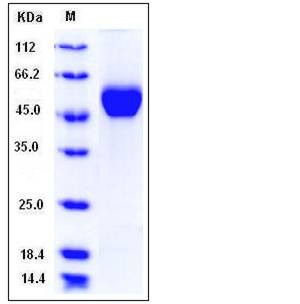 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human LUM (NP_002336.1) (Met 1-Asn 338) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Angiogenesis |Growth Factor & Receptor |proteoglycans |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Lumican, a prototypic leucine-rich proteoglycan with keratan sulfate side chains, is a major component of the cornea, dermal, and muscle connective tissues. In these bifunctional molecules, the protein moiety binds collagen fibrils and the highly charged hydrophilic glycosaminoglycans regulate interfibrillar spacings. Lumican is the major keratan sulfate proteoglycan of the cornea but is also distributed in interstitial collagenous matrices throughout the body. Lumican regulates collagenous matrix assembly as a keratan sulfate proteoglycan in the cornea and is also present in the connective tissues of other organs and embryonic corneal stroma as a glycoprotein. Lumican may regulate collagen fibril organization and circumferential growth, corneal transparency, and epithelial cell migration and tissue repair. lumican expressed in injured epithelium may modulate cell behavior such as adhesion or migration, thus contributing to corneal epithelial wound healing. Lumican plays a crucial role in the regulation of collagen assembly into fibrils in various connective tissues and serve as a definitive link between a necessity for lumican in the development of a highly organized collagenous matrix and corneal transparency. |
| Reference |
