Human MAD2L1 / MAD2 Protein (His Tag)
HSMAD2,MAD2
- 100ug (NPP4068) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12798-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | HSMAD2,MAD2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human MAD2L1 consisting of 221 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 25.6 kDa. It migrates as an 28 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 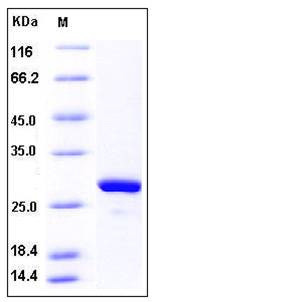 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human MAD2L1 (Q13257) (Met 1-Asp 205) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Cell cycle |Cell division |Spindle |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, 20% glycerol, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD2A, also known as HsMAD2, Mitotic arrest deficient 2-like protein 1, MAD2-like protein 1, MAD2L1 and MAD2, is a nucleus and cytoplasm protein which belongs to the MAD2 family. MAD2L1 is a component of the spindle-assembly checkpoint that prevents the onset of anaphase until all chromosomes are properly aligned at the metaphase plate. MAD2L1 is required for the execution of the mitotic checkpoint which monitors the process of kinetochore-spindle attachment and inhibits the activity of the anaphase promoting complex by sequestering CDC20 until all chromosomes are aligned at the metaphase plate. MAD2L1 has two highly different native conformations, an inactive open conformation that cannot bind CDC20 and that predominates in cytosolic monomers, and an active closed conformation. MAD2L1 in the closed conformation preferentially dimerizes with another molecule in the open conformation, but can also form a dimer with a molecule in the closed conformation. Formation of a heterotetrameric core complex containing two molecules of MAD1L1 and of MAD2L1 in the closed conformation promotes binding of another molecule of MAD2L1 in the open conformation and the conversion of the open to the closed form, and thereby promotes interaction with CDC20. |
| Reference |
