Human MANF / ARMET Protein (His Tag)
ARMET,ARP
- 100ug (NPP4069) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11324-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ARMET,ARP |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human MANF consists of 169 amino acids and migrates as an approximately 20 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| predicted N | Leu 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 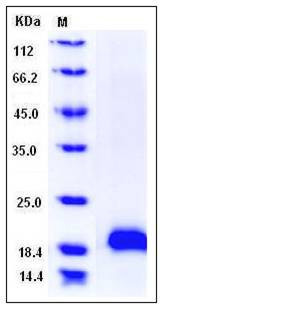 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human MANF (NP_006001.3) extracellular domain (Met 1-Leu 179) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurology process |Growth and Development |Neurotrophic Factor & Receptor |Other Neurotrophic Factors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor, also known as Protein ARMET, Arginine-rich protein, MANF and ARMET, is a secreted protein which belongs to the ARMET family. ARMET selectively promotes the survival of dopaminergic neurons of the ventral mid-brain. It modulates GABAergic transmission to the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. ARMET enhances spontaneous, as well as evoked, GABAergic inhibitory postsynaptic currents in dopaminergic neurons. ARMET inhibits cell proliferation and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced cell death. The N-terminal region of ARMET may be responsible for neurotrophic activity while the C-terminal region may play a role in the ER stress response. MANF reduces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and has neurotrophic effects on dopaminergic neurons. Intracortical delivery of recombinant MANF protein protects tissue from ischemic brain injury. MANF has been described as a survival factor for dopaminergic neurons. MANF expression was widespread in the nervous system and non-neuronal tissues. In the brain, relatively high MANF levels were detected in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus and cerebellar Purkinje cells. The widespread expression of MANF together with its evolutionary conserved nature and regulation by brain insults suggest that it has important functions both under normal and pathological conditions in many tissue types. |
| Reference |
