Human MAP1D / Methionine Aminopeptidase 1D Protein (His Tag)
MAP 1D,MAP1D,MetAP 1D,Metap1l
- 100ug (NPP2330) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10883-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | MAP 1D,MAP1D,MetAP 1D,Metap1l |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human MAP1D consists of 303 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 33.4 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 36 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 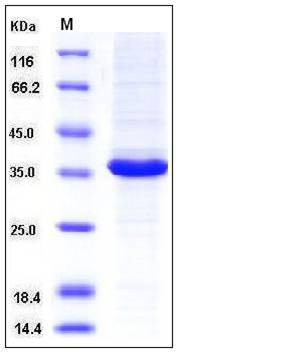 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human MAP1D (NP_954697.1) (Arg 44-Ala 335) was expressed, with an initial Met at the N-terminus and a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measure by its ability to remove methionine from a fluorogenic peptide substrate H-Met-Gly-Pro-AMC, R&D Systems, Catalog#ES017. The resulting GP-AMC is cleaved by human DPPIV/CD26, R&D Systems, Catalog#1180SE . The specific activity is >30 pmoles/min/μg . |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Protein Trafficking |Nuclear Import / Export |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Methionine aminopeptidase 1D, also known as MAP1D, is a member of the peptidase M24A family. N-terminal methionine removal is an important cellular process required for proper biological activity, subcellular localization, and eventual degradation of many proteins. The enzymes that catalyze this reaction are called Methionine aminopeptidases (MAPs). MAP1D is overexpressed in colon cancer cell lines and colon tumors as compared to normal tissues (at protein level). Downregulation of MAP1D expression by shRNA in HCT-116 colon carcinoma cells reduces anchorage-independant growth in soft agar. MAP1D binds two cobalt ions per subunit. The true nature of the physiological cofactor is under debate. MAP1D is also active with zinc, manganese or divalent ions. MAP1D removes the amino-terminal methionine from nascent proteins. It may also play an important role in colon tumorigenesis. |
| Reference |
