Human MEP1A / PPHA Protein (His Tag)
PPHA
- 100ug (NPP4075) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10133-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | PPHA |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human MEP1A (pro form) consists of 591 amino acids with the predicted molecular mass of 67.7 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, rh MEP1A migrates as an approximately 80 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Val 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 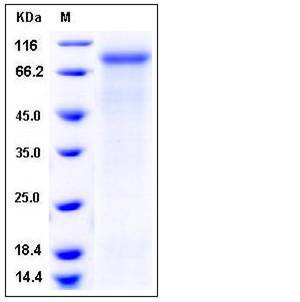 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human MEP1A (NP_005579.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Gln 601) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolism processes |Apoptosis | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Meprin A subunit alpha, also known as MEP1A, and Endopeptidase-2, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the peptidase M12A family. MEP1A contains one EGF-like domain, one MAM domain, and one MATH domain. Meprins are unique plasma membrane and secreted metalloproteinases that are highly regulated at the transcriptional and post-translational levels. Meprin alpha and beta subunits are abundantly expressed in kidney and intestinal epithelial cells, are secreted into the urinary tract and intestinal lumen, and are found in leukocytes and cancer cells under certain conditions. Meprins are capable of proteolytically degrading extracellular matrix proteins, proteolytically processing bioactive proteins, and play a role in inflammatory processes. Meprin A and B are highly regulated, secreted and cell-surface homo- and hetero-oligomeric enzymes. Meprins are abundantly expressed in kidney and intestine. The multidomain alpha and beta subunits have high sequence identity. They have very different substrate specificities, oligomerization potentials and are differentially regulated. Meprin A appears to be an important therapeutic target and urinary excretion appears to be a potential biomarker of acute kidney injury ( AKI ). |
| Reference |
