Human METTL1 Protein (His Tag)
C12orf1,TRM8,TRMT8,YDL201w
- 100ug (NPP4080) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11525-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | C12orf1,TRM8,TRMT8,YDL201w |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human METTL1 consisting of 241 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 28 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 30 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 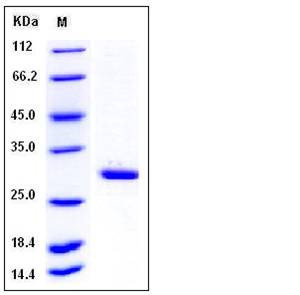 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human METTL1 (NP_005362.3) (Asp 32-Gln 265) was expressed, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 0.5M NaCl, 20% glycerol, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | tRNA (guanine-N(7)-)-methyltransferase, also known as Methyltransferase-like protein 1, tRNA (m7G46)-methyltransferase and METTL1, is a nucleus protein which belongs to the methyltransferase superfamily and TrmB family. METTL1 gene, has been identified by its sequence similarity to the yeast ORF YDL201w. The human cDNA and the genomic structure of METTL1 have been analyzed. The transcript contains 1292 nucleotides and codes for a protein of 276 amino acids. The METTL1 gene product shows high sequence similarities to putative proteins from mouse, Drosophila melanogaster, Arabidopsis thaliana, Caenorhabditis elegans, and yeast (39.8% identity between all six species). Computer analyses of the deduced protein sequence reveal two highly conserved amino acid motifs, one of which is typical for methyltransferases. Both motifs are also present in hypothetical proteins from eubacteria. Disruption of the homologous yeast ORF YDL201w shows that the gene is at least not essential for vegetative growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| Reference |
