Human MMP-3 Protein
CHDS6,MMP-3,SL-1,STMY,STMY1,STR1
- 100ug (NPP4086) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10467-HNAE |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | CHDS6,MMP-3,SL-1,STMY,STMY1,STR1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human MMP3 consisting of 256 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 29 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 34 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 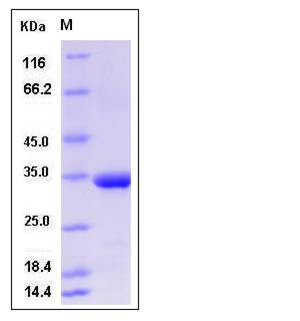 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human MMP3 (AAA36321.1) N-terminal fragment (Tyr 18-Thr 272) was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate, Mca-RPKPVE-Nva-WR-K(Dnp)-NH2, AnaSpec, Catalog # 27114. The specific activity is >300 pmoles/min/μg. (Activation description: The proenzyme needs to be activated by Chymotrypsin for an activated form) |
| Research Area | Cancer |Cell cycle |Proteolytic enzymes|Metalloprotease & Regulator |Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 10mM CaCL2, 1uM ZnCL2, 50mM NaCl, 0.5% Brij35, pH 7.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Matrix metallopeptidase 3 (abbreviated as MMP3) is also known as stromelysin 1 and progelatinase. MMP3 is a member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family whose members are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, tissue remodeling, and disease processes including arthritis and metastasis. As a secreted zinc-dependent endopeptidase, MMP3 exerts its functions mainly in extracellular matrix. This protein is activated by two major endogenous inhibitors: alpha2-macroglobulin and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases (TIMPs). MMP3 plays a central role in degrading collagen types II, III, IV, IX, and X, proteoglycans, fibronectin, laminin, and elastin. In addition, MMP3 can also active other MMPs such as MMP1, MMP7, and MMP9, rendering MMP3 crucial in connective tissue remodeling. Dysregulatoin of MMPs has been implicated in many diseases including arthritis, chronic ulcers, encephalomyelitis and cancer. Synthetic or natural inhibitors of MMPs result in inhibition of metastasis, while up-regulation of MMPs led to enhanced cancer cell invasion. |
| Reference |
