Human MOG Protein (aa 30-149, His Tag)
BTN6,BTNL11,MOGIG2,NRCLP7
- 100ug (NPP1653) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10364-H08E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | BTN6,BTNL11,MOGIG2,NRCLP7 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human MOG comprises 127 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 15 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 19 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 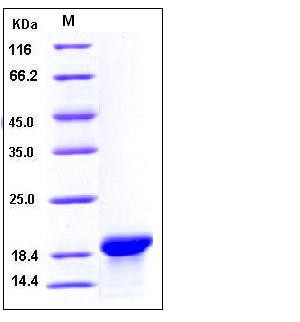 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human MOG (NP_996532.2) (Gly 30-Tyr 149) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus and an additional Met at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurology process |Neurodegeneration and Neurodegenerative Disease |Multiple sclerosis |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) is a transmembrane protein belonging to immunoglobulin superfamily, and contains an Ig-like domain followed by two potential membrane-spanning regions. MOG is expressed only in the CNS with very low content (approximately 0.1% total proteins) in oligodendrogliocyte membrane. Three possible functions for MOG were suggested: (a) a cellular adhesive molecule, (b) a regulator of oligodendrocyte microtubule stability, and (c) a mediator of interactions between myelin and the immune system, in particular, the complement cascade. A direct interaction might exist between the membrane-associated regions of MOG and the myelin-specific glycolipid galactocerebroside (Gal-C), and such an interaction may have important consequences regarding the membrane topology and function of both molecules. It is considered that MOG is an autoantigen capable to produce a demyelinating multiple sclerosis-like disease in experimental animals. |
| Reference |
