Human NAA10 / ARD1A Protein
ARD1,ARD1A,ARD1P,DXS707,MCOPS1,NAA10,NATD,OGDNS,TE2
- 100ug (NPP2358) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14293-HNCB |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | ARD1,ARD1A,ARD1P,DXS707,MCOPS1,NAA10,NATD,OGDNS,TE2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human ARD1A consists of 237 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 26.6 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 31 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gly |
| SDS-PAGE | 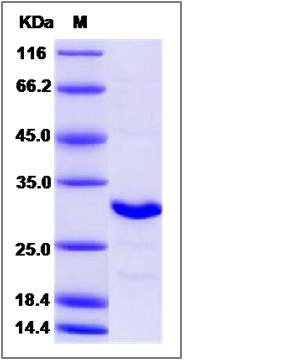 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human ARD1A (P41227) (Met1-Ser 235) was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolic signaling pathways |Amino acid metabolism | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | ARD1 is a member of the 20-kDa ARF protein family. It is a multifunctional protein. ARD1 has an 18-kDa ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) domain at the C-terminus (amino acids 403-574), and a 46-kDa N-terminal domain (amino acids 1-402). The C-terminal region of ARD1 may be involved in the formation of both ARD1-ARD1 and ARD1-NAT1 complexes. ARD1 and NAT1 genes are required for the expression of an N-terminal protein acetyltransferase. This activity is required for full repression of the silent mating type locus HML, for sporulation, and for entry into G0. Recombinant ARD1 (amino acids 1-574) or its RING finger domain (amino acids 1-110) produced polyubiquitylated proteins when incubated in vitro with a mammalian E1, an E2 enzyme, ATP, and ubiquitin. |
| Reference |
