Human NAALADL1 Protein (His Tag)
I100,NAALADASEL,NAALADL1
- 100ug (NPP4100) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11146-H07H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | I100,NAALADASEL,NAALADL1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human NAALADL1comprises 728 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 80 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, rh NAALADL1 migrates as an approximately 90 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 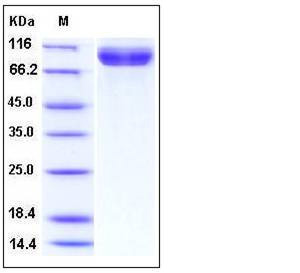 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human NAALADL1 (NP_005459.2) (Pro 29-Leu 740) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | N-acetylated-alpha-linked acidic dipeptidase-like protein, also known as NAALADL1, NAALADase L, and Ileal dipeptidylpeptidase, is a Single-pass type I I membrane protein and a member of the peptidase M28 family and M28B subfamily. NAALADase L is mainly expressed in the distal small intestine. It is also expressed in the spleen and testis and Weakly expressed in the brain, locating mainly to the brain stem, amygdala, thalamus and ventral striatum. NAALADase L is a chloride-activated, membrane bound, metallopeptidase that cleaves the endogenous neuropeptide N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate (NAAG). NAAG acts as a partial NMDA agonist as well as a full agonist at the presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 (mGluR3), where it acts to reduce glutamate release. NAALADase L also exhibits a dipeptidyl-peptidase IV type activity. NAALADase inhibition may be a novel therapeutic approach to reduce or inhibit heightened aggressiveness, and possibly to treat aggressive behavior associated with psychiatric disorders. |
| Reference |
