Human NAPG / Gamma SNAP Protein (His Tag)
NAPG, SNAPG
- 100ug (NPP2359) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P14709-H07E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | NAPG, SNAPG |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human NAPG consists of 327 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 36.6 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 37 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 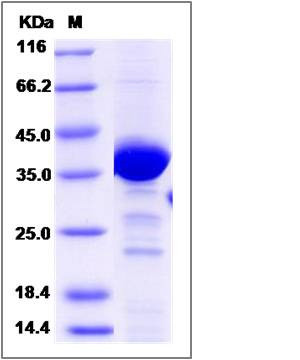 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human NAPG (AAH01889.1) (Met1-Cys312) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Trafficking |Vesicle Transport |SNAPs & SNAREs |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 10% Glycerol, 1mM DTT, pH 8.0. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | NAPG, also known as gamma SNAP, belongs to the SNAP family. SNAPs enable N-ethyl-maleimide-sensitive fusion protein (NSF) to bind to target membranes. NSF and SNAPs appear to be general components of the intracellular membrane fusion apparatus, and their action at specific sites of fusion must be controlled by SNAP receptors particular to the membranes being fused. NAPG mediates platelet exocytosis and controls the membrane fusion events of this process. It is required for vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. |
| Reference |
