Human NCF2 / NCF-2 / P67phox Protein
NCF-2,NOXA2,P67-PHOX,P67PHOX
- 100ug (NPP2361) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P15669-HNCB |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | NCF-2,NOXA2,P67-PHOX,P67PHOX |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human NCF2 consists of 528 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 59.9 KDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 60 KDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gly |
| SDS-PAGE | 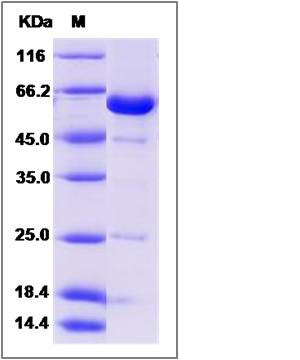 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human NCF2 (AAH01606.1) (Met1-Val526) was expressed and purified with two additional amino acids (Gly & Pro) at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Cancer |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 300mM NaCl, pH 8.0. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | NCF2, also known as NCF-2 and p67phox, is a subunit of the multi-protein NADPH oxidase complex. NCF2, NCF1, and a membrane bound cytochrome b558 are required for activation of the latent NADPH oxidase. This oxidase produces a burst of superoxide which is delivered to the lumen of the neutrophil phagosome. Mutations in NCF2 gene, as well as in other NADPH oxidase subunits, can result in chronic granulomatous disease, a disease that causes recurrent infections by catalase-positive organisms. |
| Reference |
