Human NCR2 / NKp44 / CD336 Protein (His Tag)
CD336,dJ149M18.1,LY95,NK-p44,NKP44,RP1-149M18.2
- 100ug (NPP4103) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11550-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD336,dJ149M18.1,LY95,NK-p44,NKP44,RP1-149M18.2 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human NCR2 consists of 180 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 20 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 37 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 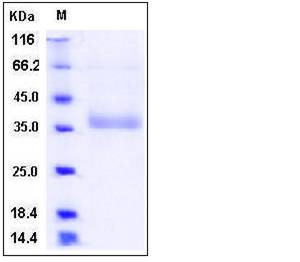 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human NCR2 (NP_004819.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Pro 190) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | +ssRNA Virus|Flaviviridae|West Nile Virus (WNV)|WNV infection associated|WNV host receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 2 (NCR2), also known as Natural killer cell p44-related protein (NKp44), or CD336, is a member of the natural cytotoxicity receptor (NCR) family, which composed of one Ig-like extracellular domain, a transmembrane segment, and a cytoplasmic domain. It is a novel transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the Immunoglobulin superfamily characterized by a single extracellular V-type domain. The cytoplasmic domain of NKp44 also contains a sequence that matches the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) consensus. This Cytotoxicity-activating receptor that may contribute to the increased efficiency of activated natural killer (NK) cells to mediate tumor cell lysis. NKp44 is selectively expressed by IL-2-activated NK cells and may contribute to the increased efficiency of activated NK cells to mediate tumor cell lysis. Tumor cell recognition of the mutated NKp44 proteins was significantly reduced and correlated with their lower recognition of heparin. |
| Reference |
