Human NETO1 / BTCL1 Protein (His Tag)
BCTL1,BTCL1
- 100ug (NPP4107) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11562-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | BCTL1,BTCL1 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human NETO1 consists of 333 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 38 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 46 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Thr 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 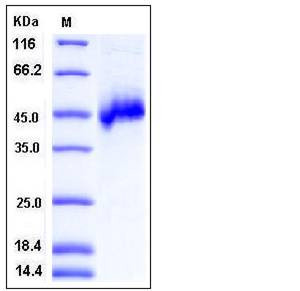 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human NETO1 isoform 3 (NP_620416.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Thr 344) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Sensory System |Visual system |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Neuropilin tolloid-like 1 (NETO1), a complement C1r/C1s, Uegf, Bmp1 (CUB) domain-containing transmembrane protein, is a novel component of the NMDAR complex critical for maintaining the abundance of NR2A-containing NMDARs in the postsynaptic density. The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR), a major excitatory ligand-gated ion channel in the central nervous system (CNS), is a principal mediator of synaptic plasticity. Both NETO1 and NETO2 share an identical and unique domain structure thus representing a novel subfamily of CUB- and LDLa-containing proteins. The cytoplasmic domains of NETO1 and NETO2 are not homologous to other known protein sequences but contain a conserved FXNPXY-like motif, which is essential for the internalization of clathrin coated pits during endocytosis or alternatively, may be implicated in intracellular signaling pathways. NETO1 and NETO2, have marked effects on receptor properties, increasing further the potential diversity of Kainate receptors (KARs) functional properties. NETO1 involves in the development and/or maintenance of neuronal circuitry. NETO1 regulates long-term NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity and cognition, at least in the context of spatial learning and memory. |
| Reference |
