Human β-NGF / Beta-NGF Protein
Beta-NGF,HSAN5,NGFB
- 100ug (NPP1669) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11050-HNAC |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | CHO Stable Cells |
| Synonyms | Beta-NGF,HSAN5,NGFB |
| Molecular Weight | The mature recombinant human β-NGF consists of 118 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 13.2 kDa. β-NGF exists as a non-disulfide linked homodimer in solution. |
| predicted N | Ser 122 |
| SDS-PAGE | 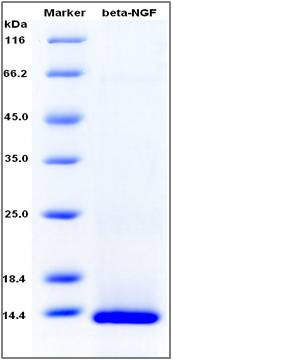 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human β-NGF (NP_002497.2) (Ser 122-Arg 239) was expressed. |
| Bio-activity | Measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.2-2 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Hormones |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM NaAc, 150mM NaCl, pH 5.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Nerve growth factor (NGF) is important for the development and maintenance of the sympathetic and sensory nervous systems. NGF protein was identified as a large complex consisting of three non-covalently linked subunits, α, β, and γ, among which, the β subunit, called β-NGF (beta-NGF), was demonstrated to exhibits the growth stimulating activity of NGF protein. NGFB/beta-NGF gene is a member of the NGF-beta family and encodes a secreted protein which homodimerizes and is incorporated into a larger complex. NGF protein acts via at least two receptors on the surface of cells (TrkA and p75 receptors) to regulate neuronal survival, promote neurite outgrowth, and up-regulate certain neuronal functions such as mediation of pain and inflammation. In addition, previous studies indicated that NGF may also have an important role in the regulation of the immune system. |
| Reference |
