Human NMNAT2 / NMNAT-2 Protein (His Tag)
C1orf15,PNAT2
- 100ug (NPP2371) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11399-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | C1orf15,PNAT2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human NMNAT2 consists of 317 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 35.8 kDa. The recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 35 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 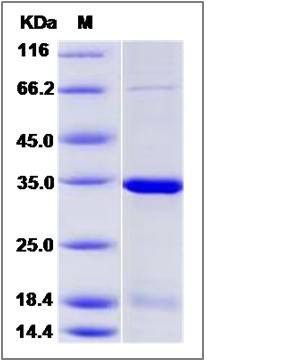 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human NMNAT2 (Q9BZQ4-1)(Met1-Gly307) was fused with a polyhistide tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Vitamins / minerals |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 5mM DTT, 10% glycerol, pH 8.0. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | NMNAT2, also known as NMNAT-2, belongs to the nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT) enzyme family. NMNAT is a central enzyme in NAD+ biosynthesis, transferring the adenylyl moiety of ATP to nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) or nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NaMN) resulting in the formation of NAD+ or NaAD+ and the release of pyrophosphate. NMNAT2 is predominantly expressed in human pancreas, insulinoma as well as in the brain, especially in the cerebrum, cerebellum, occipital lobe, frontal lobe, temporal lobe and putamen. Immunofluorescence microscopy localized endogenous NMNAT2 to the Golgi apparatus in human cell line. Endogenous NMNAT2 seem to be a labile axon survival factor, because specific depletion of NMNAT2 is sufficient to induce Wallerian-like degeneration of uninjured axons which endogenous NMNAT1 and NMNAT3 cannot prevent. Thus endogenous NMNAT2 represents an exciting new therapeutic target for axonal disorders. |
| Reference |
