Human Neuroligin-3 / NLGN3 Protein (His Tag)
HNL3
- 100ug (NPP2366) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11160-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | HNL3 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human NLGN3 consists of 663 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 74 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rh NLGN3 is approximately 100-110 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 38 |
| SDS-PAGE | 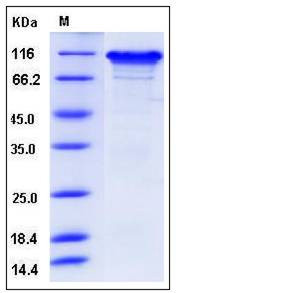 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human NLGN3 isoform 2 (Q9NZ94-2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Ser 689) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Cell Type Marker in Neurodevelopment |Glial Cell Markers |Oligodendrocyte marker |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Neuroligin 3 (NLGN3) is a member of the type-B carboxylesterase/lipase family. Neuroligins (NLGNs) are a family of presumptive postsynaptic cell adhesion molecules. Neuroligins (NLs) constitute a family of cell-surface proteins that interact with neurexins (beta-Nxs), another class of neuronal cell-surface proteins, one of each class functioning together in synapse formation. Neuroligins control the formation and functional balance of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in hippocampal neurons. NLGN1 and NLGN2 isoforms are concentrated at glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses, respectively, but the cellular expression and synaptic localization of the endogenous. NLGN3 was enriched in brain, where NLGN3 protein levels increased during postnatal development, coinciding with the peak of synaptogenesis. The NLGN3 is a synaptic adhesion molecule that is a shared component of glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses. Mutations in NLGN3 gene may be associated with autism and Asperger syndrome. |
| Reference |
