Human Nicastrin / NCSTN Protein (His Tag)
APH2,ATAG1874,KIAA0253,NCSTN,RP11-517F10.1
- 100ug (NPP4116) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11183-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | APH2,ATAG1874,KIAA0253,NCSTN,RP11-517F10.1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human NCSTN consists of 647 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 72.4 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh NCSTN is approximately 110-120 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Asn 34 |
| SDS-PAGE | 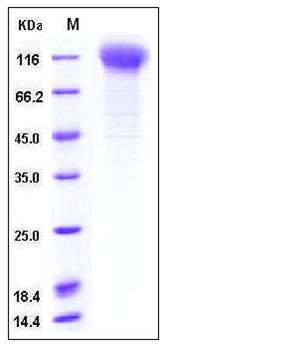 |
| Purity | > 93 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human NCSTN (NP_056146.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Glu 669) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Angiogenesis |Angiogenic Factor |Notch Family |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Nicastrin (NCST, or NCT), a single-pass membrane glycoprotein that harbors a large extracellular domain, is an essential component of the gamma-secretase complex. Several lines of evidence indicate that the members of these complexes could also contribute to the control of cell death. NCT controls cell death via phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt and p53-dependent pathways and that this function remains independent of the activity and molecular integrity of the gamma-secretase complexes. Increasing evidences have shown that Nicastrin/NCSTN plays a crucial role in gamma-cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). The glycoprotein Nicastrin is an essential component of the gamma-secretase complex, a high molecular weight complex which also contains the presenilin proteins, Aph-1 and Pen-2. The gamma-secretase complex is not only involved in APP processing but also in the processing of an increasing number of other type I integral membrane proteins. As the largest subunit of the gamma-secretase complex, Nicastrin plays a crucial role in its activation. Inhibition of NCSTN demonstrated an altered gamma-cleavage activity, suggesting its potential implication in developing Alzheimer's disease (AD). In addition, Nicastrin can function to maintain epithelial to mesenchymal transition during breast cancer progression. Anti-nicastrin polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies were able to decrease notch1 and vimentin expression and reduced the invasive capacity of breast cancer cells in vitro. |
| Reference |
