Human Noggin / NOG Protein (Fc Tag)
Noggin,SYM1,SYNS1
- 100ug (NPP4121) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10267-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Noggin,SYM1,SYNS1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human Noggin/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein after removal of the signal peptide. Each monomer comprises 443 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 49.8 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhNoggin/Fc monomer is approximately 58-62 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 28 |
| SDS-PAGE | 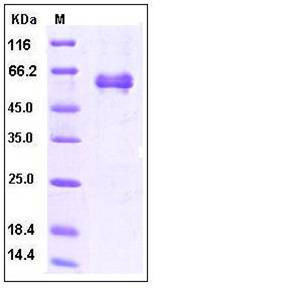 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human Noggin precursor (NP_005441.1) (Met 1-Cys 232) was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its ability to inhibit BMP2-induced alkaline phosphatase production by MC3T3-E1 cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 1.5-2.0 μg /mL in the presence of 0.25-0.5 μg/mL of BMP-2. 2. Measured by its ability to inhibit BMP4-induced alkaline phosphatase production by MC3T3-E1 cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.1-0.6 μg/mL in the presence of 50 ng/mL of hBMP4. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cytokines & Growth Factors |Cytokine & Receptor |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Superfamily |TGF-beta Superfamily Modulators |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 100mM Glycine, 10mM NaCl, 50mM Tris, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Noggin is a secreted protein involved at multiple stages of vertebrate embryonic development including neural induction and is known to exert its effects by inhibiting the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-signaling pathway. It binds several BMPs with very high (picomolar) affinities, with a marked preference for BMP2 and BMP4 over BMP7. By binding tightly to BMPs, Noggin prevents BMPs from binding their receptors. Noggin binds the bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP) such as BMP-4 and BMP-7, and inhibits BMP signaling by blocking the molecular interfaces of the binding epitopes for both type I and type II receptors. Interaction of BMP and its antagonist Noggin governs various developmental and cellular processes, including embryonic dorsal-ventral axis, induction of neural tissue, formation of joints in the skeletal system and neurogenesis in the adult brain. Noggin plays a key role in neural induction by inhibiting BMP4, along with other TGF-β signaling inhibitors such as chordin and follistatin. Mouse knockout experiments have demonstrated that noggin also plays a crucial role in bone development, joint formation, and neural tube fusion. |
| Reference |
