Human OSTM1 Protein (His Tag)
GIPN,GL,HSPC019,OPTB5
- 100ug (NPP4135) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10913-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | GIPN,GL,HSPC019,OPTB5 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human OSTM1 comprises 264 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 29.7 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the recombinant protein migrates as an approximately 40-50 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ala 32 |
| SDS-PAGE | 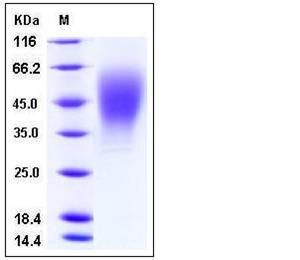 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human OSTM1 (NP_054747.2) (Met 1-Pro 284) was expressed, fused with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Cell cycle |Cell Differentiation |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Osteopetrosis-associated transmembrane protein 1 (OSTM1) is a Single-pass type I membrane protein. It is expressed in many hematopoietic cells of the myeloid and lymphoid B- and T-lineages. The analysis of OSTM1 association with CLCN7 demonstrated that OSTM1 requires CLCN7 to localize to lysosomes, whereas the formation of a CLCN7-OSTM1 complex is required to stabilize CLCN7. The researches found that OSTM1 plays a major role in myelopoiesis and lymphopoiesis and provided evidence of a crosstalk mechanism between hematopoietic cells for osteoclast activation. Thus, OSTM1 has a important role in osteoclast function and activation. The loss of function of OSTM1 results in deregulation of multiple hematopoietic lineages in addition to osteoclast lineage, OSTM1-defect patients display the most severe recessive osteopetrotic phenotype and die at early ages. Furthermore, it is suggested that OSTM1 has a primary role in neural development not related to lysosomal dysfunction. The canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway may be a molecular basis for OSTM1 mutations and severe autosomal recessive osteopetrosis (ARO). |
| Reference | 1. Chalhoub, N. et al., 2003, Nat Med. 9 (4): 399-406. 2. Quarello, P. et al., 2004, J Bone Miner Res. 19 (7): 1194-1199. 3. Lange, PF. et al., 2006, Nature. 440 (7081): 220-223 4. Maranda, B. et al., 2008, J Bone Miner Res. 23 (2): 296-300. 5. Feigin, ME.et al., 2008, Cell Signal. 20 (5): 949-957. 6. Pata, M.et al., 2008, J Biol Chem. 283 (45): 30522-30530. |
