Human PARP-1 / PARP Protein (His Tag)
ADPRT,ADPRT1,ARTD1,pADPRT-1,PARP,PARP-1,PPOL
- 100ug (NPP4143) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11040-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | ADPRT,ADPRT1,ARTD1,pADPRT-1,PARP,PARP-1,PPOL |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human PARP1 consists of 1024 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 114.5 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rhPARP1 is approximately 100-110 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 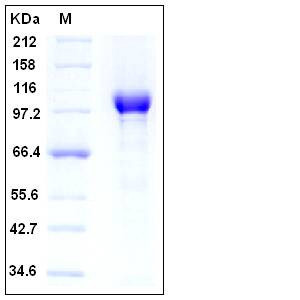 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | The amino acids corresponding to the full length of human PARP1 (NP_001609.2) (Met 1-Trp 1014) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 2. Immobilized human PARP1 at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human HSP70, The EC50 of biotinylated human HSP70 is 0.035 μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Other Related Intracellular Topics |Cellular Senescence and Pathways in Aging |Apoptosis |Nuclear | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1(PRAP1), also known as NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase 1(ADPRT), is a chromatin-associated enzyme which modifies various nuclear proteins by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. The ADP-D-ribosyl group of NAD+ is transferred to an acceptor carboxyl group on a histone or the enzyme itself, and further ADP-ribosyl groups are transferred to the 2'-position of the terminal adenosine moiety, building up a polymer with an average chain length of 20-30 units. The poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation modification is critical for a wide range of processes, including DNA repair, regulation of chromosome structure, transcriptional regulation, mitosis and apoptosis. PARP1 is demonstrateed to mediate the poly(ADP-ribose) ation of APLF (aprataxin PNK-like factor) and CHFR (checkpoint protein with FHA and RING domains), two representative proteins involved in the DNA damage response and checkpoint regulation. Further, It has been suggested that DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK), another component of DNA repair, suppresses PARP activity, probably through direct binding and/or sequestration of DNA-ends which serve as an important stimulator for both enzymes. PARP1 inhibitors is thus proposed as a targeted cancer therapy for recombination deficient cancers, such as BRCA2 tumors. |
| Reference |
